Introduction
In recent months, the global market for commodity resins has witnessed a noteworthy trend – a continuous decline in prices. This article delves into this phenomenon, with a focus on the prominent reductions seen in various types of resins, such as Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), Polystyrene (PS), and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC). By analyzing the forces driving these price adjustments, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of the resin market.
The declining resin prices can be attributed to various external factors, including global feedstock cost variations, changes in demand patterns, and strategic decisions by suppliers. In this context, it’s crucial to assess how each type of resin has reacted to these factors and what implications this holds for the future.
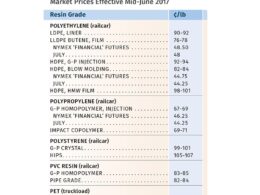
Polyethylene (PE) Prices Lower
Polyethylene (PE) prices have experienced a significant drop, specifically a further decline of 4¢/lb in January alone, following a cumulative decrease of 11¢/lb over two months. Industry experts, such as Michael Greenberg and Mike Burns from Resin Technology, Inc. (RTi), foresee additional declines in February and March. Burns highlights that spot PE prices, which have dropped over 20¢/lb, are approaching their lowest levels, with off-grade resin prices ranging between 57-63¢/lb.
The reduction in global PE prices, which have decreased by 15-20¢/lb since October, is a precursor for similar trends in domestic contract prices. Burns emphasizes that at the current feedstock prices, domestic PE prices should hover around 60¢/lb. Despite the price reductions, supply remains abundant, with active spot PE trading. The purchasing behavior post-Chinese New Year will likely influence price stabilization, as domestic prices are expected to align with global market standards once crude oil prices stabilize.
Polypropylene (PP) Prices Tumble
January witnessed a substantial drop of 10¢/lb in Polypropylene (PP) prices, aligning with the 12¢/lb drop in propylene monomer. However, PP suppliers have retained a 2¢/lb profit margin despite falling monomer prices, with predictions suggesting stable or even slightly increased prices. Scott Newell, director of client services for PP at RTi, underscores the ongoing effort by suppliers to expand profit margins, facing a dynamically shifting and less transparent market.
Supply constraints exacerbated by technical issues and order forecasting have further affected PP’s market equilibrium. Suppliers are progressively decoupling PP pricing from monomer prices, though this effort may face challenges due to increased competition from imported low-cost PP finished goods, primarily from the Far East, Europe, and the Middle East. Newell warns that while this is currently a small percentage, its impact should not be underestimated, signaling potential market shifts.
Polystyrene (PS) Prices Decline
Polystyrene (PS) prices followed a downward trend with a 9¢/lb drop in January, marking the fifth consecutive monthly decline since September 2014, summing to a total decrease of 21¢/lb. The price reduction aligns with Mark Kallman’s projections from RTi, who noted a continuation of the trend into February with some suppliers announcing additional decreases.
This decline correlates with January’s significant benzene contract price drop of $1.17/gal, further reduced by 19¢/gal in February, and a 3¢/lb decline in ethylene contract prices. Despite a seasonal demand deceleration in the construction and recreation markets, there is potential market pick-up anticipated, along with opportunities for styrene monomer exports to Europe, creating a dynamic yet cautious outlook for PS prices.
Resistance to PVC Price Hikes
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) market saw a 2¢/lb price reduction in January, extending the 5¢ decline from the last months of 2014, in tandem with lower ethylene contract prices. Despite this, PVC suppliers have proposed price hikes for February and March, described by Kallman from RTi as a “defensive move” to mitigate further price drops amidst maintenance outages scheduled for the first quarter.
However, the success of these proposed increases remains uncertain, with Kallman expressing skepticism about their implementation and even the possibility for further price reductions. Nonetheless, there is optimism for growth in PVC demand tied to the upcoming construction season, highlighting the potential for demand-driven stabilization in the near future.
Market Dynamics and Future Outlook
The ongoing decline in commodity resin prices reflects a broader market realignment influenced by multiple factors such as global pricing pressures, supply-demand balance, and raw material cost structures. As suppliers navigate these dynamics, strategic pricing adjustments and new market opportunities, such as exports and import competition, will play critical roles.
Moving forward, stakeholders in the resin industry must remain vigilant and adaptive, aligning their procurement and sales strategies with emerging trends. The implications of these price changes span across supply chain operations, influencing everything from production planning to customer negotiations, underscoring the need for proactive market engagement.
#Commodity #Resin #Prices #Drop
Última atualização em 25 de abril de 2025